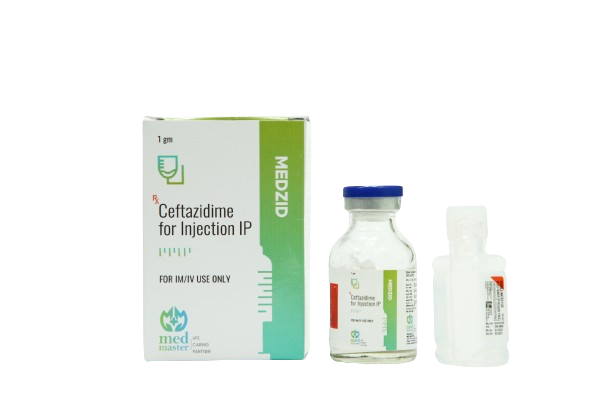
Description
Ceftazidime (as Ceftazidime Pentahydrate)
Ceftazidime is an antibiotic drug that is used in the treatment of several bacterial infections of the urinary tract, respiratory tract, brain, bones and joints, ears, throat, skin, and soft tissue. Bacterial infection is a situation in which harmful bacteria increase in the body and cause infection. It can spread diseases to any part of the body and increases very quickly. Ceftazidime injection does not work against infections caused by the virus.
The antibiotic, Ceftazidime, in ceftazidime injection disrupts the synthesis of the cell wall that protects bacteria from external harm. Therefore, it damages the bacterial cell wall and kills the bacteria.
The injection of Ceftazidime will be administered by a qualified healthcare professional; therefore, it must not be self-administered. At times, you may feel redness and swell together with a vein, red raised skin rash that may be itchy, burning, painful inflammation or swelling at the site of injection, and diarrhea. Most of these side effects of Ceftazidime injection do not need medical attention and will subside on their own over time, while in case of persistence of these side effects or developing them worse, please visit your doctor immediately.
Medical Benefits:-
Ceftazidime injection is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, which acts on both aerobic and anaerobic gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. It is used for the treatment of several bacterial infections of the urinary tract, respiratory tract, brain, bones and joints, ears, throat, skin, and soft tissue. Ceftazidime injection disrupts the process by which bacteria synthesize the protective cell wall structure required to preserve themselves. Thereby causing bacterial cell wall destruction and subsequent bacterial death. Moreover, Ceftazidime injection may also be applied to a condition such as bacterium-related fever in an individual who possesses fewer white blood cells in his/her blood; further, it is also applied in cases like males undergoing prostate surgery as a prevention measure for bacteria-related diseases.
How Does Ceftazidime Work?
Ceftazidime is an antibiotic. It works to kill bacteria by preventing the formation of the bacterial protective covering, known as the cell wall, which is essential for the survival of the bacteria.
Side Effects:-
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Hypersensitivity
- Injection site inflammation
- Inflammation of vein
- Abdominal pain
Precautions:-
- He, being your doctor has prescribed Ceftazidime to treat an infection and avert the deteriorating symptoms of you.
- Complete a full treatment course. Refrain from missing single doses and, even if relieved, do not stop taking medication early as infection may become uncontrollable.
- Taking it with a meal will eliminate the risk of stomach upset.
- Diarrhea may be a side effect, but it should resolve when your course is finished. Let your doctor know if it does not stop or if you see blood in your stools.
- Avoid alcohol during your treatment with Ceftazidime as this may lead to increased side effects.
- Stop taking Ceftazidime and seek medical attention immediately if you develop a rash, itching, swelling of the face and mouth, or experience difficulty breathing.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ):-
Q. What organisms does Ceftazidime cover?
Ceftazidime has activity against all pseudomonas, anaerobes, and staphylococcus bacteria. The drug may not have efficacy on the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Q. How is Ceftazidime administered?
Administration Ceftazidime is taken under the administration of a well-trained health worker or doctor. It should not be self-administered. The appropriate dose depends on the condition that you are receiving treatment for. Your doctor will decide on that. Always heed your doctor’s instructions carefully for the maximum benefit of Ceftazidime.
Q. Can the use of Ceftazidime cause diarrhea?
Yes, it does cause diarrhea. Ceftazidime is an antibiotic that kills bad bacteria. It also kills the good bacteria in your stomach or intestine and leads to diarrhea. If diarrhea persists, discuss it with your doctor.